Cloudflare: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zovi (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Create a tunnel) |
Zovi (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
= Cloudflare = | = Cloudflare = | ||
== Argo Tunnel == | == Argo Tunnel == | ||
| + | === Short === | ||
| + | https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-apps/configuration/config | ||
| + | |||
| + | Without specifying --config, cloudflared will default to reading ~/.cloudflared/config.yml. An example config.yml for the above command could look like: | ||
| + | |||
| + | hostname: test.example.com | ||
| + | url: http://localhost:8096 | ||
| + | logfile: /var/log/cloudflared.log | ||
| + | hello-world: false | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=== Linux === | === Linux === | ||
| Zeile 8: | Zeile 21: | ||
https://developers.cloudflare.com/argo-tunnel/reference/service/ | https://developers.cloudflare.com/argo-tunnel/reference/service/ | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Zeile 117: | Zeile 128: | ||
Deleting the Tunnel also invalidates the credentials file associated with that Tunnel, meaning those connections can not be re-established. | Deleting the Tunnel also invalidates the credentials file associated with that Tunnel, meaning those connections can not be re-established. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Arguments ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tunnel commands | ||
| + | |||
| + | All tunnel-related commands are prefixed with tunnel. For example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | cloudflared tunnel --origincert ~/cert.pem --config ~/tunnel.yaml run mytunnel | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Tunnel-related commands include creating, deleting and running tunnels with | ||
| + | |||
| + | cloudflared tunnel create <TUNNELNAME> | ||
| + | cloudflared tunnel delete <TUNNELNAME> | ||
| + | cloudflared tunnel run <TUNNELNAME> | ||
| + | You can also list all tunnels with | ||
| + | |||
| + | cloudflared tunnel list | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tunnel commands | ||
| + | --config | ||
| + | --autoupdate-freq | ||
| + | --no-autoupdate | ||
| + | --origincert | ||
| + | --no-tls-verify | ||
| + | --metrics | ||
| + | --metrics-update-freq | ||
| + | --tag | ||
| + | --loglevel | ||
| + | --proto-loglevel | ||
| + | --retries | ||
| + | --pidfile | ||
| + | --logfile | ||
| + | --help | ||
| + | --version | ||
| + | |||
| + | --config | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default | ||
| + | --config value ~/.cloudflared/config.yml | ||
| + | Specifies a config file in YAML format. | ||
| + | |||
| + | --autoupdate-freq | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default | ||
| + | --autoupdate-freq 24h | ||
| + | Autoupdate frequency. See also --no-autoupdate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --no-autoupdate | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default | ||
| + | --no-autoupdate false | ||
| + | Disables periodic check for updates, restarting the server with the new version. See also --autoupdate-freq. Restarts are performed by spawning a new process that connects to the Cloudflare edge. On successful connection, the old process will gracefully shut down after handling all outstanding requests. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --origincert | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default Environment Variable | ||
| + | --origincert value ~/.cloudflared/cert.pem TUNNEL_ORIGIN_CERT | ||
| + | Specifies the Tunnel certificate for one of your zones, authorizing the client to serve as an origin for that zone. A certificate is required to use Argo Tunnel. You can obtain a certificate by using the login command or by visiting https://dash.cloudflare.com/argotunnel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --no-tls-verify | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default | ||
| + | --no-tls-verify false | ||
| + | Disables TLS verification of the certificate presented by your origin. Will allow any certificate from the origin to be accepted. The connection from your machine to Cloudflare's Edge is still encrypted and verified using TLS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --metrics | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default Environment Variable | ||
| + | --metrics value localhost: TUNNEL_METRICS | ||
| + | Address to query for usage metrics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --metrics-update-freq | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default Environment Variable | ||
| + | --metrics-update-freq duration 5s TUNNEL_METRICS_UPDATE_FREQ | ||
| + | Frequency to update tunnel metrics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --tag | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Environment Variable | ||
| + | --tag KEY=VALUE TUNNEL_TAG | ||
| + | Custom tags used to identify this tunnel, in format KEY=VALUE. Multiple tags may be specified by delimiting them with commas e.g. KEY1=VALUE1,KEY2=VALUE2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --loglevel | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default Environment Variable | ||
| + | --loglevel value info TUNNEL_LOGLEVEL | ||
| + | Specifies the verbosity of logging. The default info is not noisy, but you may wish to run with warn in production. Available options: panic fatal error warn info debug | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --proto-loglevel | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default Environment Variable | ||
| + | --proto-loglevel warn TUNNEL_PROTO_LOGLEVEL | ||
| + | Specifies the verbosity of the HTTP/2 protocol logging. Any value below warn is noisy and should only be used to debug low-level performance issues and protocol quirks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --retries | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Default Environment Variable | ||
| + | --retries value 5 TUNNEL_RETRIES | ||
| + | Maximum number of retries for connection/protocol errors. Retries use exponential backoff (retrying at 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 seconds by default) so increasing this value significantly is not recommended. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --pidfile | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Environment Variable | ||
| + | --pidfile value TUNNEL_PIDFILE | ||
| + | Write the application's PID to this file after the first successful connection. Mainly useful for scripting and service integration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --logfile | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax Environment Variable | ||
| + | --logfile value TUNNEL_LOGFILE | ||
| + | Save application log to this file. Mainly useful for reporting issues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --help | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax | ||
| + | --help | ||
| + | Shows help text. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | --version | ||
| + | |||
| + | Syntax | ||
| + | --version | ||
| + | Prints the version number and build date. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Login command | ||
| + | cloudflared tunnel login | ||
| + | Opens a special section of the Cloudflare dashboard for obtaining a Tunnel certificate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It should open your browser automatically and prompt you to log in to your Cloudflare account (unless you previously logged in with 'Remember me' selected). If running cloudflared on a server, you will be given an URL that you can visit on another machine. After logging in, a list of your zones will appear. Select the zone you want to use Argo Tunnel with. After confirming your authorization, the certificate should be sent to the Tunnel client and saved to .cloudflared/cert.pem in your user folder. If this process fails for any reason, the certificate will instead be downloaded by your browser and you will have to copy the file manually to that location. You can also obtain a Tunnel certificate independently of this command by visiting https://dash.cloudflare.com/argotunnel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Service commands | ||
| + | cloudflared service install | ||
| + | |||
| + | cloudflared service uninstall | ||
| + | Install or uninstall cloudflared as a system service. The details of service installation depend on the OS you are using. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Update command | ||
| + | cloudflared update | ||
| + | Looks for a new version on the official download server. If a new version exists, updates the agent binary and quits. Otherwise, it does nothing. To determine if an update happened in a script, check for error code 64. | ||
Version vom 19. Februar 2021, 17:06 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Cloudflare
Argo Tunnel
Short
https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-apps/configuration/config
Without specifying --config, cloudflared will default to reading ~/.cloudflared/config.yml. An example config.yml for the above command could look like:
hostname: test.example.com url: http://localhost:8096 logfile: /var/log/cloudflared.log hello-world: false
Linux
run as Service
https://developers.cloudflare.com/argo-tunnel/reference/config/
https://developers.cloudflare.com/argo-tunnel/reference/service/
Windoof
Install cloudflared
Once cloudflared is installed:
Navigate to the Downloads folder. Right-click on the ZIP folder and select Extract All to extract the executable. Next, open PowerShell. Navigate to the same Downloads folder. Run the cloudflared.exe executable as an administrator to confirm the installation, replacing the path in the example below with the specifics of your directory:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\cloudflared-stable-windows-amd64> .\cloudflared.exe --version
https://developers.cloudflare.com/cloudflare-one/connections/connect-apps/install-and-setup/setup
Updating cloudflared
You can update cloudflared by running the following command.
cloudflared update
The update will cause cloudflared to restart which would impact traffic currently being served. You can perform zero-downtime upgrades by using Cloudflare's Load Balancer product or by using multiple cloudflared instances.
Authenticate cloudflared
Follow these steps to authenticate cloudflared:
1. Log in to your Cloudflare account with the following command:
cloudflared tunnel login
2. The command will attempt to open a browser window and prompt you to authenticate with your Cloudflare account.
If running on a headless system, copy the link and paste it into a browser.
3. Once authenticated, Cloudflare will return a certificate file, cert.pem, that will give this instance of cloudflared the ability to:
- Create and delete Tunnels
- Modify DNS records in your account
The file is required if you want to:
- Create new Tunnels
- Change DNS routing from cloudflared
The file is not required if you want to:
- Run an existing Tunnel
- Manage routing from the Cloudflare dashboard
Create a tunnel
NOTE: Tunnels created in this method do not currently display in the Traffic tab of the Cloudflare dashboard. These connections will be added to the dashboard in a future release.
To create a Tunnel, run the following command:
cloudflared tunnel create <NAME>
Replace <NAME> with the name you want to give to the Tunnel. The name assigned can be any string and does not need to relate to the hostname where traffic will be served.
This command will create a Tunnel with the name provided and associate it with a UUID. The relationship between the UUID and the name is persistent. The command will not create a connection at this point.
Creating a Tunnel generates a credentials file for that specific Tunnel. This file is distinct from the cert.pem file. To run the Tunnel without managing DNS from cloudflared, you only need the credentials file.
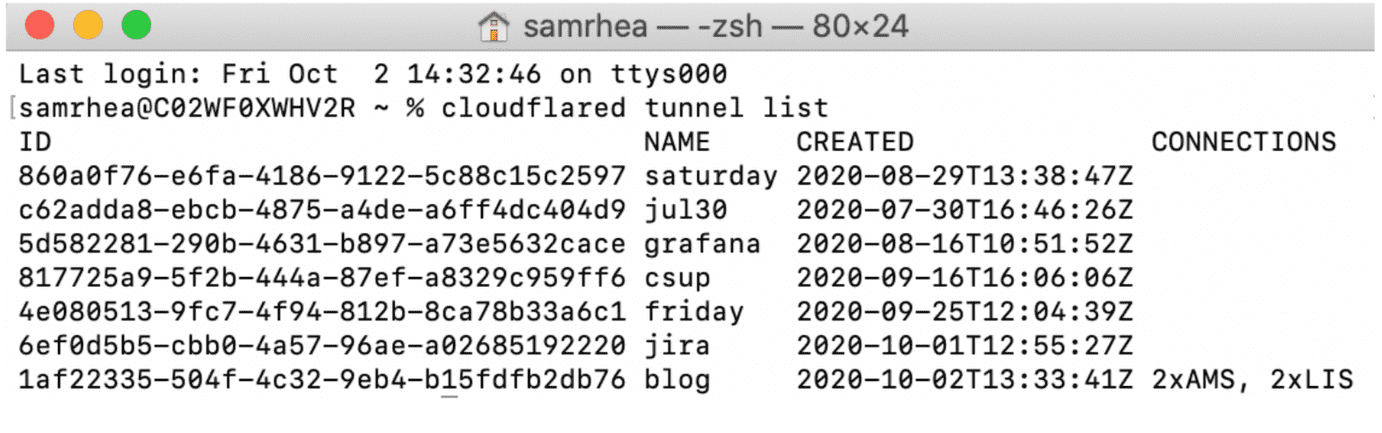
List available Tunnels
cloudflared can list all created Tunnels in your account, as well as those actively connected to Cloudflare, by running the following command:
cloudflared tunnel list
Note: the command requires the cert.pem file.
Revoke and delete a Tunnel
Revoke and delete a Tunnel
You can delete an existing Tunnel with cloudflared. To delete a Tunnel, run the following command:
cloudflared tunnel delete <NAME>
NOTE: The command requires the cert.pem file.
If there are still active connections on that Tunnel, then you will have to force the deletion with:
cloudflared tunnel delete -f <NAME>
This will cause those connections to be dropped.
Deleting the Tunnel also invalidates the credentials file associated with that Tunnel, meaning those connections can not be re-established.
Arguments
Tunnel commands
All tunnel-related commands are prefixed with tunnel. For example:
cloudflared tunnel --origincert ~/cert.pem --config ~/tunnel.yaml run mytunnel
Tunnel-related commands include creating, deleting and running tunnels with
cloudflared tunnel create <TUNNELNAME> cloudflared tunnel delete <TUNNELNAME> cloudflared tunnel run <TUNNELNAME>
You can also list all tunnels with
cloudflared tunnel list
Tunnel commands --config --autoupdate-freq --no-autoupdate --origincert --no-tls-verify --metrics --metrics-update-freq --tag --loglevel --proto-loglevel --retries --pidfile --logfile --help --version
--config
Syntax Default
--config value ~/.cloudflared/config.yml
Specifies a config file in YAML format.
--autoupdate-freq
Syntax Default
--autoupdate-freq 24h
Autoupdate frequency. See also --no-autoupdate.
--no-autoupdate
Syntax Default
--no-autoupdate false
Disables periodic check for updates, restarting the server with the new version. See also --autoupdate-freq. Restarts are performed by spawning a new process that connects to the Cloudflare edge. On successful connection, the old process will gracefully shut down after handling all outstanding requests.
--origincert
Syntax Default Environment Variable
--origincert value ~/.cloudflared/cert.pem TUNNEL_ORIGIN_CERT
Specifies the Tunnel certificate for one of your zones, authorizing the client to serve as an origin for that zone. A certificate is required to use Argo Tunnel. You can obtain a certificate by using the login command or by visiting https://dash.cloudflare.com/argotunnel.
--no-tls-verify
Syntax Default
--no-tls-verify false
Disables TLS verification of the certificate presented by your origin. Will allow any certificate from the origin to be accepted. The connection from your machine to Cloudflare's Edge is still encrypted and verified using TLS.
--metrics
Syntax Default Environment Variable
--metrics value localhost: TUNNEL_METRICS
Address to query for usage metrics.
--metrics-update-freq
Syntax Default Environment Variable
--metrics-update-freq duration 5s TUNNEL_METRICS_UPDATE_FREQ
Frequency to update tunnel metrics.
--tag
Syntax Environment Variable
--tag KEY=VALUE TUNNEL_TAG
Custom tags used to identify this tunnel, in format KEY=VALUE. Multiple tags may be specified by delimiting them with commas e.g. KEY1=VALUE1,KEY2=VALUE2.
--loglevel
Syntax Default Environment Variable
--loglevel value info TUNNEL_LOGLEVEL
Specifies the verbosity of logging. The default info is not noisy, but you may wish to run with warn in production. Available options: panic fatal error warn info debug
--proto-loglevel
Syntax Default Environment Variable
--proto-loglevel warn TUNNEL_PROTO_LOGLEVEL
Specifies the verbosity of the HTTP/2 protocol logging. Any value below warn is noisy and should only be used to debug low-level performance issues and protocol quirks.
--retries
Syntax Default Environment Variable
--retries value 5 TUNNEL_RETRIES
Maximum number of retries for connection/protocol errors. Retries use exponential backoff (retrying at 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 seconds by default) so increasing this value significantly is not recommended.
--pidfile
Syntax Environment Variable
--pidfile value TUNNEL_PIDFILE
Write the application's PID to this file after the first successful connection. Mainly useful for scripting and service integration.
--logfile
Syntax Environment Variable
--logfile value TUNNEL_LOGFILE
Save application log to this file. Mainly useful for reporting issues.
--help
Syntax
--help
Shows help text.
--version
Syntax
--version
Prints the version number and build date.
Login command
cloudflared tunnel login
Opens a special section of the Cloudflare dashboard for obtaining a Tunnel certificate.
It should open your browser automatically and prompt you to log in to your Cloudflare account (unless you previously logged in with 'Remember me' selected). If running cloudflared on a server, you will be given an URL that you can visit on another machine. After logging in, a list of your zones will appear. Select the zone you want to use Argo Tunnel with. After confirming your authorization, the certificate should be sent to the Tunnel client and saved to .cloudflared/cert.pem in your user folder. If this process fails for any reason, the certificate will instead be downloaded by your browser and you will have to copy the file manually to that location. You can also obtain a Tunnel certificate independently of this command by visiting https://dash.cloudflare.com/argotunnel.
Service commands
cloudflared service install
cloudflared service uninstall
Install or uninstall cloudflared as a system service. The details of service installation depend on the OS you are using.
Update command
cloudflared update
Looks for a new version on the official download server. If a new version exists, updates the agent binary and quits. Otherwise, it does nothing. To determine if an update happened in a script, check for error code 64.